

Understanding IGU (Insulated Glass Unit) A Key Component in Modern Construction
Insulated Glass Units, commonly referred to as IGUs, are a crucial innovation in the construction and architecture industry. These units consist of multiple glass panes separated by a spacer and sealed to create a barrier that dramatically improves thermal insulation. Given the increasing focus on energy efficiency and sustainability in building design, IGUs have gained significant attention for their numerous benefits.
What is an IGU?
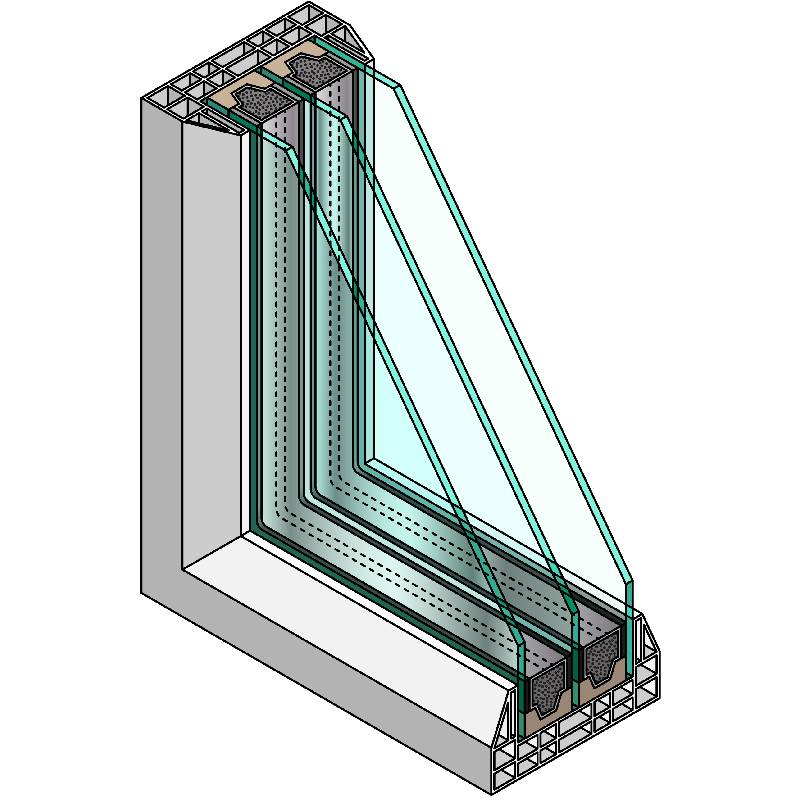
An IGU typically consists of two or more glass panes that are hermetically sealed around the edges, creating an air or gas-filled space in between. This space acts as an insulating layer, reducing the transfer of heat between the interior and exterior environments. The most common arrangement is double glazing (two panes of glass), although triple glazing (three panes) is also prevalent in areas with more extreme temperatures.
Thermal Performance
One of the primary advantages of IGUs is their exceptional thermal performance. By minimizing heat transfer, they can help maintain a building's internal temperature, reducing reliance on heating and cooling systems. This not only leads to lower energy bills for occupants but also contributes to a decrease in carbon emissions, supporting global efforts to combat climate change.
Additionally, IGUs can be filled with noble gases like argon or krypton, which further enhances their insulating properties. These gases have lower thermal conductivity than air, meaning they resist heat transfer even more effectively, offering enhanced performance compared to standard double glazing.
Sound Insulation
IGUs also provide significant sound insulation benefits. The air or gas space between the panes can effectively dampen noise from outside, creating a quieter indoor environment. This is particularly beneficial in urban settings or near busy roads, where noise pollution can detract from the comfort of living or working spaces.
Safety and Security
In terms of safety and security, IGUs are designed to withstand impacts better than single-pane glass. The multiple layers of glazing can be tempered or laminated for added strength, helping to prevent shattering. This makes IGUs an ideal choice for residential homes, commercial buildings, and public facilities where safety is a priority.
Aesthetic Versatility
Not only are IGUs functional, but they also offer aesthetic versatility. They can be customized in terms of thickness, color, and texture to meet the specific design requirements of any project. Architects and builders can choose from a variety of finishes to create an appealing exterior while benefiting from the energy efficiency that IGUs provide.
Environmental Considerations
With a global push towards sustainable construction practices, IGUs support LEED (Leadership in Energy and Environmental Design) certification and other green building certifications. Their energy-efficient nature significantly contributes to the overall sustainability of a building. By using IGUs, builders can reduce the structural load on HVAC systems and decrease overall energy consumption during a building's lifecycle.
Conclusion
In conclusion, Insulated Glass Units (IGUs) represent a significant advancement in modern construction, offering a range of benefits including superior thermal and sound insulation, enhanced safety and security, aesthetic flexibility, and a positive environmental impact. As building codes become stricter and the demand for energy-efficient buildings continues to grow, the role of IGUs will only become more essential. Their unique properties make them a vital component for any architect or builder aiming to push the boundaries of design while promoting sustainability and comfort. With ongoing advancements in glazing technologies, the future of IGUs looks promising, making them an integral part of contemporary architecture and construction.