Float glass is an essential material in modern architecture and design, providing both functionality and aesthetic appeal. With various types to suit diverse applications, understanding the different types of float glass can significantly enhance project outcomes.
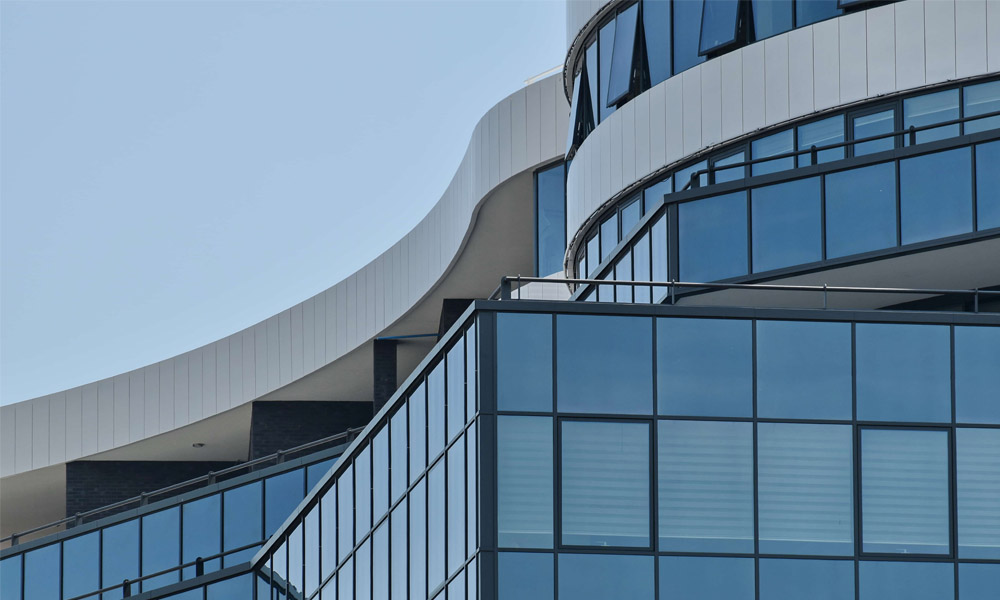

Clear float glass is the most prevalent and provides a baseline for comparison. Manufactured by floating molten glass on a bed of molten tin, clear float glass offers excellent clarity and minimal distortion. Its versatility makes it a staple for windows, doors, and partitions, where natural light and visibility are key considerations.
Tinted float glass stands out for its ability to reduce solar heat gain, essential for energy efficiency in buildings. By incorporating metallic oxides during production, this glass minimizes glare and enhances privacy without compromising aesthetics. Available in shades such as bronze, gray, and green, it allows architects to control the visual impact and energy performance of a structure.
Low-iron float glass, sometimes known as ultra-clear or extra-clear glass, is another variant sought for its superior clarity. By reducing the iron content in the glass mix, the greenish tint typical of standard float glass is minimized, providing unparalleled clarity and color neutrality. This makes low-iron glass an ideal choice for applications where color representation and transparency are crucial, such as in display cases, aquariums, and solar panels.
Reflective float glass offers both functional and aesthetic benefits. A metallic coating on one surface of the glass reflects a portion of the sunlight, reducing solar heat and glare. This makes it invaluable in high-rise buildings where controlling heat and light is pivotal. Furthermore, the reflective surface can give buildings a modern, sleek appearance.
types of float glass
In the realm of safety and security,
laminated float glass is indispensable. Formed by bonding two or more layers of glass with interlayers of polyvinyl butyral (PVB), laminated glass holds together when shattered. This quality not only enhances safety by preventing dangerous shards but also offers improved sound insulation and UV protection. It is favored in applications such as automotive windshields, skylights, and hurricane-resistant windows.
Tempered float glass undergoes a thermal tempering process that significantly increases its strength compared to regular glass. When broken, it fractures into small, less dangerous pieces, making it a safer option. This attribute makes it suitable for use in environments prone to impact, such as shower doors, glass facades, and balustrades.
Lastly, self-cleaning float glass is becoming increasingly popular for its low maintenance and sustainability benefits. With a special coating that breaks down organic dirt through a natural photocatalytic process utilizing sunlight, this glass significantly reduces the need for cleaning. Ideal for hard-to-reach windows and high-rise buildings, self-cleaning glass helps maintain a spotless appearance, reducing labor and maintenance costs.
Selecting the appropriate type of float glass relies heavily on understanding the specific requirements of a project. From energy efficiency and safety to aesthetics and functionality, each type offers distinct advantages. An expertise-driven approach ensures optimal performance and longevity, while fostering an aesthetically pleasing and energy-efficient environment. By integrating these considerations into the design and construction phases, architects and builders can leverage the unique properties of float glass to create structures that are not only beautiful but also highly functional and sustainable.



