

Understanding Low-E2 Glass Enhancing Energy Efficiency in Modern Architecture
As the world continues to grapple with the challenges of energy conservation and environmental sustainability, the construction industry is increasingly turning to advanced materials that promote efficiency. Among these, Low-E2 (Low Emissivity) glass stands out as a pivotal innovation. This specialized type of insulating glass offers significant advantages in terms of thermal performance and energy savings, making it an essential component in modern architectural design.
What is Low-E2 Glass?
Low-E2 glass is a type of glass that has been coated with a thin layer of metallic oxides. This coating is applied to one side of the glass, which enhances its ability to reflect infrared energy while allowing visible light to pass through. The “2” in Low-E2 refers to the specific manner in which the glass is designed to perform, particularly in situations where energy efficiency is paramount. The application of Low-E glass serves to reduce heating and cooling costs significantly while improving comfort levels within buildings.
How Low-E2 Glass Works
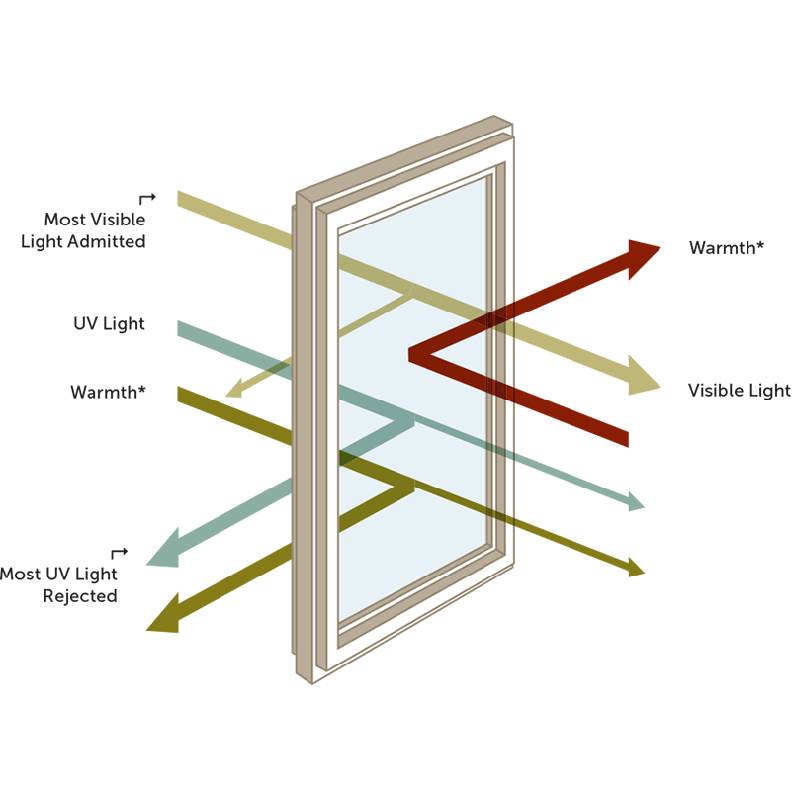
The functionality of Low-E2 glass is rooted in its unique ability to manage solar heat gain and radiant heat loss. In colder months, the coating reflects interior heat back into the building, preventing it from escaping through the windows. During warmer months, Low-E2 glass reflects a significant portion of solar energy away from the building, helping to maintain a cooler interior without relying heavily on air conditioning systems.
The low emissivity coating also minimizes the heat that radiates from the glass surface. This effect diminishes the need for additional heating sources, leading to notable reductions in energy consumption. Furthermore, Low-E2 glass can protect interior furnishings and decor from harmful ultraviolet (UV) rays, helping to preserve aesthetics and prolong their life span.
Benefits of Low-E2 Glass
1. Energy Efficiency The primary benefit of Low-E2 glass is its ability to enhance energy efficiency. By minimizing heat loss in winter and reducing heat gain in summer, it significantly lowers heating and cooling costs for residential and commercial building owners alike.
2. Comfort The use of Low-E2 glass leads to improved comfort within indoor environments. By regulating temperatures and reducing drafts, occupants experience a more stable and pleasant living or working atmosphere.
3. Environmental Impact With the growing emphasis on sustainability, Low-E2 glass plays a crucial role in reducing the carbon footprint of buildings. By consuming less energy for heating and cooling, buildings equipped with this glass contribute to lower greenhouse gas emissions.
4. Aesthetic Appeal Low-E2 glass allows architects and designers to create large, expansive windows without compromising energy efficiency. This offers opportunities for abundant natural light without the drawbacks of excessive heat gain or loss.
5. Durability The coatings on Low-E2 glass are designed to be durable and long-lasting. They withstand the elements better than standard glass, maintaining their effectiveness over time.
Applications of Low-E2 Glass
Low-E2 glass is suitable for a wide range of applications, from residential homes to commercial office buildings. It is particularly beneficial in climates with extreme temperature variations, where the need for effective insulation is paramount. Architects often use it in passive solar home designs, where maximizing natural light and minimizing energy use are key goals. Additionally, Low-E2 glass is commonly used in curtain walls, skylights, and patio doors, contributing to the overall energy performance of these structures.
Conclusion
In conclusion, Low-E2 glass represents a significant advancement in building material technology that aligns with modern energy demands and environmental considerations. Its unparalleled ability to enhance energy efficiency while providing aesthetic benefits makes it a preferred choice among architects, builders, and homeowners. As the construction industry continues to evolve towards more sustainable practices, Low-E2 glass will undoubtedly play a critical role in shaping energy-efficient buildings for future generations. Embracing such innovative materials is crucial to achieving greater sustainability and comfort in our everyday lives.