

Understanding High-Performance Low-E Glass A Key to Energy Efficiency
In modern architecture and building design, energy efficiency is a top priority. One of the most innovative materials contributing to this goal is high-performance low-emissivity (low-E) glass. This specialized glass offers numerous advantages, significantly enhancing the energy efficiency of buildings while ensuring occupant comfort.
What is Low-E Glass?
Low-E glass is a type of energy-efficient glass that has been treated with a microscopically thin, transparent coating. This coating reflects heat while allowing natural light to pass through, thus facilitating a balance between illumination and temperature control. Unlike regular glass, which allows heat to escape during colder months and lets in excessive heat during warmer periods, low-E glass maintains an optimal indoor environment, reducing reliance on heating and cooling systems.
Categories of Low-E Glass
Low-E glass can be categorized into two types based on its coating soft-coat and hard-coat. Soft-coat low-E glass is made by applying the coating in a controlled environment, leading to a higher performance rating. This type of glass is highly efficient at insulating and reflects more infrared radiation than its counterpart. Hard-coat low-E glass, on the other hand, is applied during the manufacturing process and is generally more durable but slightly less efficient.
Benefits of High-Performance Low-E Glass
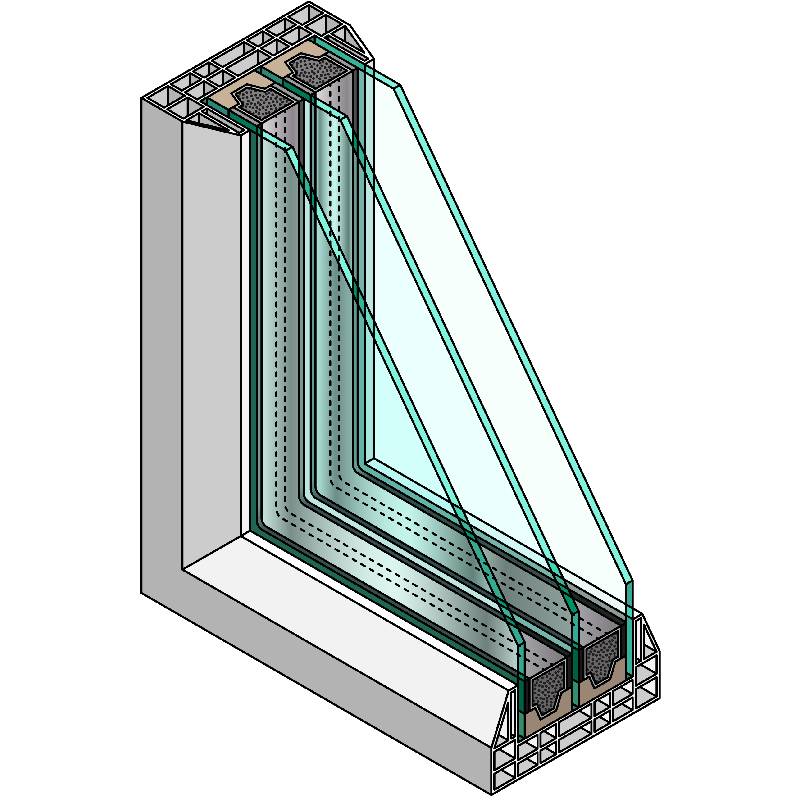
1. Energy Efficiency The primary benefit of high-performance low-E glass is its ability to significantly reduce energy consumption. By minimizing heat transfer, it ensures that less energy is used for heating in winter and cooling in summer. Studies have shown that the use of low-E glass can reduce energy costs by up to 30% in some climates.
2. UV Protection Another compelling advantage is its capability to block harmful ultraviolet (UV) rays. Unlike traditional glass, which allows a large percentage of UV radiation to penetrate, low-E glass minimizes UV exposure, protecting occupants and reducing fading of furniture and interior finishes.
3. Comfort and Indoor Quality The use of high-performance low-E glass contributes to improved indoor comfort. By maintaining stable indoor temperatures and reducing glare from direct sunlight, it enhances the quality of life for building occupants.
4. Environmental Impact As energy efficiency is closely linked to environmental sustainability, the adoption of low-E glass in buildings helps reduce carbon footprints. Lower energy consumption means fewer fossil fuels burned for heating and cooling, aiding in the fight against climate change.
5. Aesthetic Flexibility Beyond functionality, low-E glass offers architectural versatility. It can be used in various applications, including windows, doors, and facades, without compromising on aesthetics. It is available in various finishes and tints, allowing for creative design possibilities while maintaining energy-saving properties.
Conclusion
In conclusion, high-performance low-E glass is a critical innovation in modern architecture that promotes energy efficiency and enhances occupant comfort. As the world moves towards sustainable building practices, understanding and implementing such technologies is vital for architects, builders, and homeowners alike. With continuous advancements in glass technology, low-E options are likely to become even more efficient, further propelling us toward a greener future. Adopting high-performance low-E glass not only represents a smart economic choice but also a positive step towards environmental stewardship.