

Annealed Float Glass Properties, Production, and Applications
Annealed float glass is a widely-used flat glass type produced through a process known as the float glass method, which has become the industry standard since its invention in the mid-20th century. This article explores the properties, production, and various applications of annealed float glass, shedding light on its significance in modern architecture and construction.
Production Process
The float glass process involves melting raw materials, including silica sand, soda ash, and limestone, at high temperatures to create molten glass. The molten glass is then poured onto a bed of molten tin, allowing it to spread out and form a smooth, flat surface. This method ensures that the glass is uniform in thickness and free from imperfections. Once the glass has reached the desired thickness, it undergoes a slow cooling process known as annealing. This critical step allows the glass to relieve internal stresses, resulting in a product that is both stable and safe for various applications.
Properties of Annealed Float Glass
Annealed float glass is characterized by several key properties. It has excellent optical clarity, allowing for high levels of light transmission, making it ideal for windows and facades. The glass is also chemically inert, resisting discoloration and degradation over time. Additionally, annealed float glass has good thermal stability, making it suitable for environments where temperature fluctuations occur. However, it is worth noting that while annealed float glass is strong, it is also more susceptible to breakage compared to tempered glass, necessitating proper handling and installation.
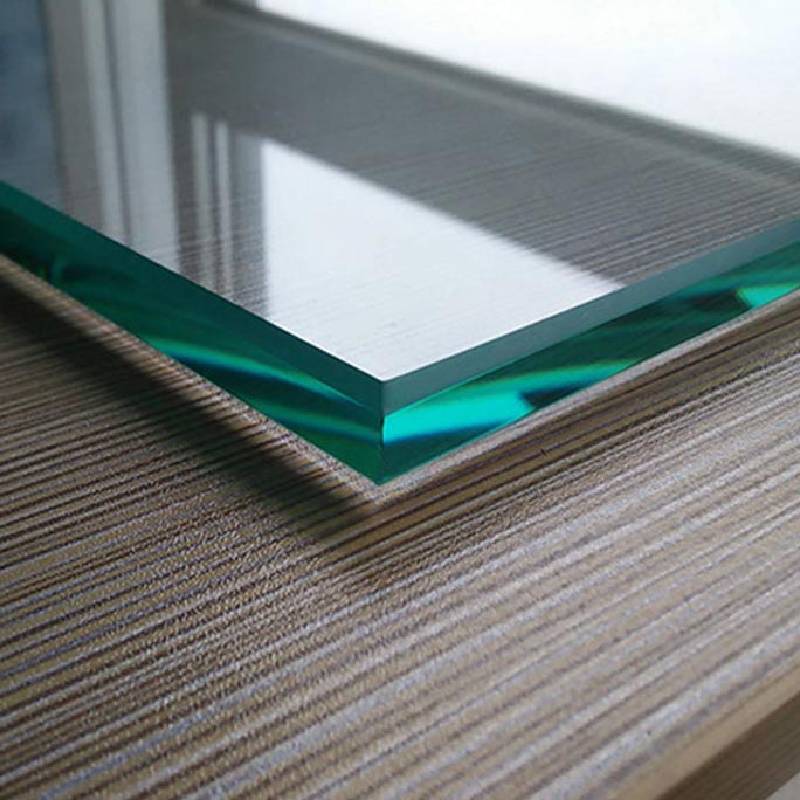
The standard thickness of annealed float glass ranges from 2mm to 19mm, catering to various decorative and functional requirements. Its availability in large sheets allows for versatility in design, making it a preferred choice for architects and designers.
Applications
The uses of annealed float glass are extensive. It plays a vital role in the construction industry, particularly in the production of windows, doors, and facades. Due to its clarity and aesthetic appeal, it is also widely used in interior design for mirrors, glass partitions, and decorative panels. In addition, annealed float glass can be found in furniture, such as tabletops and display cases, where its visual qualities can enhance the overall design.
In recent years, advancements in the processing of float glass have led to the development of low-emissivity (low-E) glass products. These specialized coatings improve thermal insulation and energy efficiency, making annealed float glass even more appealing in the context of sustainable building practices.
Conclusion
Annealed float glass is an essential material in modern construction and design, thanks to its unique properties and versatile applications. Its smooth surface and optical clarity have made it a favorite among architects, builders, and interior designers alike. While it may not possess the increased strength of tempered glass, its reliability and aesthetic qualities continue to ensure its place in a variety of use cases. As technology advances, the potential for further innovations within the realm of float glass promises exciting possibilities for the future, enhancing both functional performance and design aesthetics. In summary, annealed float glass remains a testament to modern engineering, fulfilling essential roles in enhancing the beauty and functionality of our built environments.