Float glass, the unsung hero of modern architecture and design, often goes unnoticed in everyday life, yet it plays a critical role in shaping our contemporary world. This type of glass is renowned for its versatility, clarity, and utility, making it an essential component in various applications that range from everyday household installations to advanced architectural projects. This article explores the diverse use cases of float glass, drawing on insider knowledge and authoritative insights to provide a comprehensive understanding of its applications and its transformative impact on different sectors.
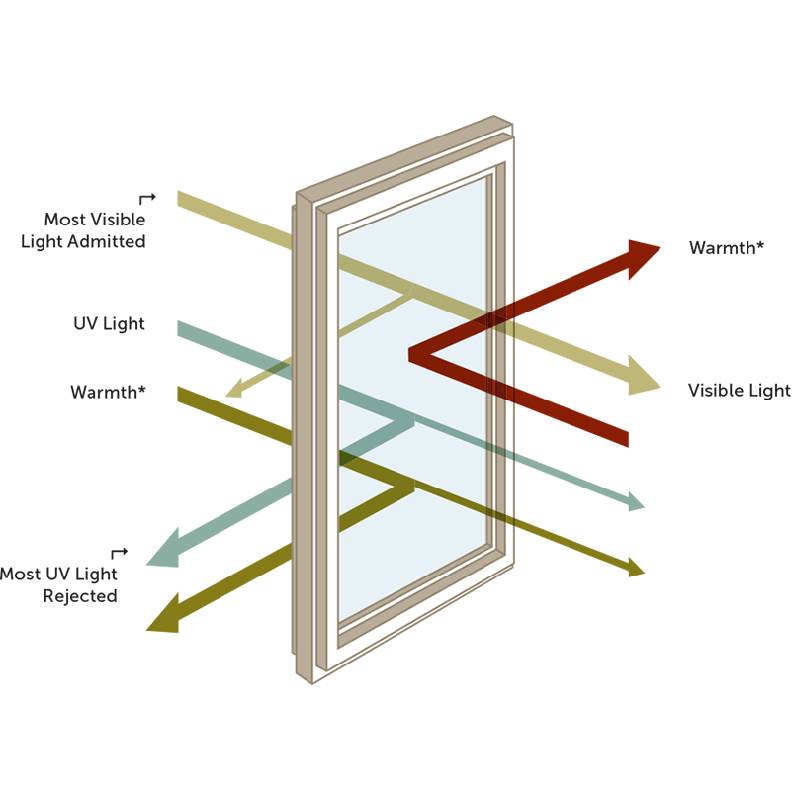
One of the primary uses of float glass is in residential and commercial building fenestration, where it serves as an essential material for windows, doors, and facades. The unparalleled clarity and smoothness of float glass enhance natural light transmission while offering unobstructed views, a feature architects and designers covet when creating spaces that blur the boundaries between indoor and outdoor environments. Additionally, float glass easily adapts to various finishes and coatings, such as low-emissivity layers, which enhance energy efficiency by insulating buildings and reducing heating and cooling costs.
Beyond standard windows and doors, float glass is crucial in producing high-performing, aesthetically pleasing building facades. Structural glazing systems, often relying on the robust properties of float glass, permit the construction of transparent or semi-transparent walls, emphasizing architectural elegance and functional daylighting. The material's ability to withstand temperature fluctuations and resist weathering further underscores its fitness for such demanding applications, solidifying its reputation for reliability and durability.
In the realm of interior design, float glass finds applications in furniture, such as tabletops, shelves, and cabinetry, where it provides a modern, minimalist aesthetic. Its versatility is further exhibited through its availability in different thicknesses and tints, allowing designers to implement diverse stylistic elements to suit specific aesthetic requirements. Moreover, the safety options available with float glass, such as tempering and laminating, increase its appeal for use in environments where both durability and safety are paramount, such as in public spaces and private residencies with children.
what is float glass used for
Automotive manufacturing is another domain that benefits significantly from the properties of float glass. In this industry, the glass is utilized for windshields, windows, and sunroofs, essential for maintaining vehicle safety and passenger comfort. Float glass in automotive applications is often laminated or tempered to enhance its strength and shatter-resistance, ensuring it meets stringent safety standards. Moreover, advancements in technology allow for the integration of features like UV protection and enhanced acoustic performance, tailored to improve the overall driving experience.
The creative industry also takes advantage of float glass, employing it in art and minimalistic sculpture due to its clear, smooth surface and ability to interact with light. Artists and artisans value float glass for its capability to be shaped and treated with various techniques, including etching, sandblasting, and staining, leading to the production of stunning visual effects. In this context,
float glass transcends its primary function as a structural material, becoming a medium for personal and cultural expression.
Finally, in the sphere of technology, float glass serves as a substrate for electronic displays, including televisions, monitors, and tablets. It provides a stable, high-quality surface for the application of pixel-based display coatings, critical in achieving high-resolution imagery. Its innate uniformity and clarity ensure that devices provide an optimal user experience, a factor increasingly significant as consumers demand superior display technologies.
In conclusion, the diverse applications of float glass stem from its intrinsic qualities of transparency, ease of manufacture, and adaptability to various enhancements. It seamlessly bridges the gap between functionality and design, solidifying its role as an indispensable material across numerous industries. As innovations continue to emerge, the potential for new applications of float glass seems boundless, promising to shape our built environment and technological interfaces in unforeseen ways. Embracing the multifaceted uses of float glass not only highlights its current importance but also sets the stage for future advancements in material science and architectural design.



