

Understanding Low-E2 Glass A Modern Solution for Energy Efficiency
In the quest for energy efficiency and sustainability, Low-E2 glass has emerged as a revolutionary building material. Its unique properties not only enhance the comfort of indoor environments but also contribute significantly to energy savings in residential and commercial buildings. This article delves into what Low-E2 glass is, how it works, and its benefits for modern architecture.
What is Low-E2 Glass?
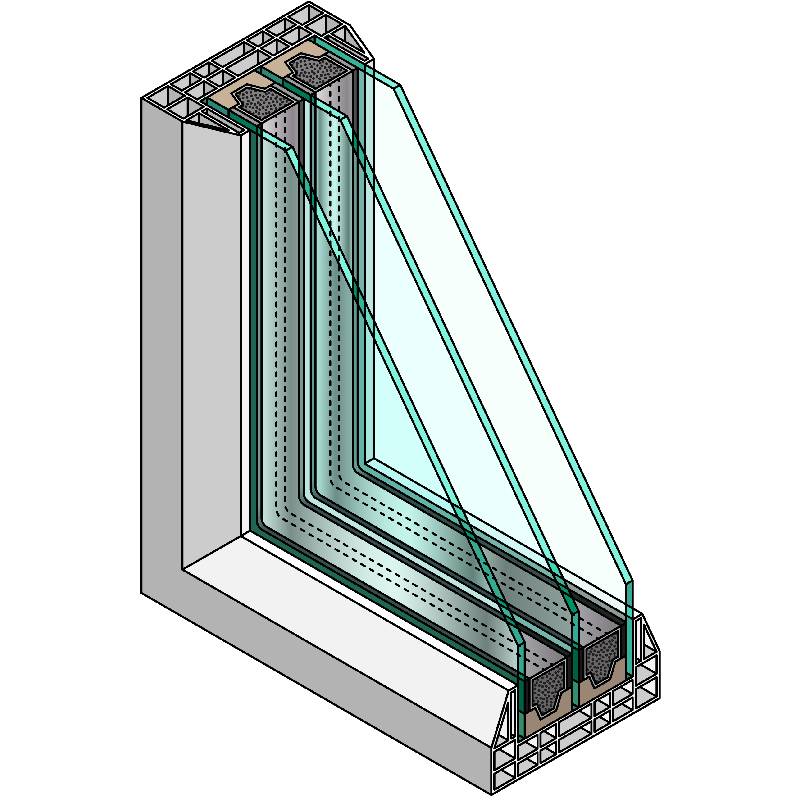
Low-E2 glass, short for low-emissivity glass, is treated with a microscopically thin, transparent coating that reflects heat and helps maintain energy efficiency. Unlike traditional glass, which allows heat to enter and escape freely, Low-E2 glass acts as a barrier to thermal transfer. This means that during the summer months, it reflects unwanted solar heat away from the building, while in the winter, it reflects interior heat back inside.
The ‘E’ in Low-E refers to the emissivity of the glass, while the ‘2’ designates a specific type of coating that enhances energy performance without compromising natural light. Low-E2 glass is an improvement on previous iterations of Low-E glass technologies, designed to provide better performance and broader applications.
How Does Low-E2 Glass Work?
The key to Low-E2 glass's performance lies in its coating. This coating is typically made from microscopic layers of metals or metallic oxides, which are applied during the manufacturing process. When sunlight strikes the glass, a portion of the energy is reflected back outside, while visible light passes through, illuminating the interior.
The performance of Low-E2 glass is measured using U-values and Solar Heat Gain Coefficient (SHGC). A lower U-value indicates less heat transfer and better insulation, while a lower SHGC means less solar heat gain, making it ideal for maintaining a comfortable indoor climate without relying heavily on heating and cooling systems.
Benefits of Low-E2 Glass
1. Energy Efficiency One of the most significant advantages of Low-E2 glass is its ability to significantly reduce energy consumption. Buildings installed with Low-E2 windows can see a decrease in heating and cooling costs by as much as 30-50%. This lower energy demand translates to reduced greenhouse gas emissions and a smaller carbon footprint.
2. Enhanced Comfort With its ability to manage heat transfer, Low-E2 glass improves indoor comfort by stabilizing temperatures year-round. It prevents cold drafts in the winter and reduces excessive heat in the summer, creating more comfortable living and working spaces.
3. UV Protection Low-E2 glass also blocks a significant percentage of harmful ultraviolet (UV) rays, which can fade furniture, carpets, and artwork. By limiting UV exposure, it helps to preserve the integrity and aesthetic quality of interior furnishings.
4. Noise Reduction The unique construction of Low-E2 glass can also contribute to sound attenuation. By installing Low-E2 windows, buildings can reduce outside noise, making interiors quiet and more conducive to productivity and relaxation.
5. Aesthetic Appeal Beyond its performance benefits, Low-E2 glass is also aesthetically pleasing. It does not compromise the clarity and brilliance of natural light, allowing architects to design buildings that are both energy-efficient and visually striking.
Conclusion
As the demand for energy-efficient building materials continues to rise, Low-E2 glass stands out as a prominent solution in modern architecture. By effectively managing heat gain and loss, filtering harmful UV rays, and providing aesthetic versatility, it addresses the needs of contemporary living while promoting sustainability. Investing in Low-E2 glass is not just a step towards saving on energy bills; it's a commitment to a greener future and a more sustainable planet. As technology continues to evolve, incorporating innovations like Low-E2 glass will be crucial in tackling the challenges of climate change and fostering energy-conscious lifestyles.