

The Advantages and Applications of Low-E Glass Materials
Low-emissivity (low-E) glass is a type of energy-efficient glass that has been designed to minimize the amount of infrared and ultraviolet light that passes through it without compromising the amount of visible light transmitted. This innovative material has become increasingly popular in residential and commercial buildings due to its energy-saving properties, enhancing comfort while contributing to sustainability. In this article, we will explore the composition, benefits, and various applications of low-E glass materials.
Composition and Technology
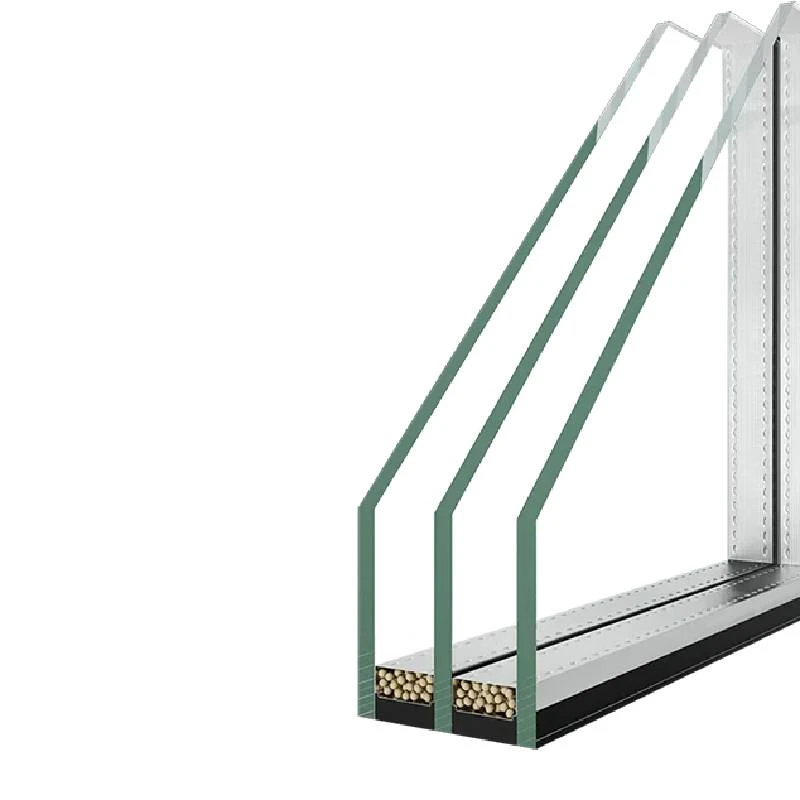
Low-E glass is coated with a thin layer of metal or metallic oxide that provides its unique properties. This coating reflects heat back into the room during cold months, while allowing sunlight to enter and warm the space. In warmer months, the coating helps reflect solar heat away from the interior, keeping buildings cooler and reducing the demand for air conditioning. The effectiveness of low-E coatings can vary, being classified into two main types first-surface and second-surface coatings, depending on their placement on the glass.
First-surface coatings are applied directly to the outer layer of the glass, while second-surface coatings are located between two layers of glass in double-glazing systems. This technology is pivotal in harnessing solar energy efficiently while maintaining indoor environmental quality.
Benefits of Low-E Glass
1. Energy Efficiency One of the primary advantages of low-E glass is its ability to enhance energy efficiency in buildings. By controlling the amount of heat that enters or leaves a space, low-E glass can significantly reduce heating and cooling costs. Buildings that utilize low-E glass often achieve better energy ratings, making them more appealing to environmentally conscious consumers.
2. Comfort Improvement Low-E glass helps maintain a more stable indoor temperature by preventing cold drafts in the winter and excessive heat in the summer. This results in enhanced overall comfort for occupants, as they can enjoy a more stable and pleasant living or working environment.
3. UV Protection The coatings on low-E glass also block a significant portion of ultraviolet (UV) rays, which can cause fading in furniture, artwork, and flooring. By reducing UV exposure, low-E glass not only helps preserve the aesthetics of interior spaces but also prolongs the lifespan of items that would otherwise be damaged by prolonged sun exposure.
4. Condensation Reduction Low-E glass can help reduce condensation buildup on windows. By maintaining a higher surface temperature on the interior side of the glass, it minimizes the likelihood of moisture accumulation, which can lead to mold growth and window degradation.
5. Sustainability By reducing energy consumption, low-E glass materials contribute to lower greenhouse gas emissions. In a world increasingly focusing on sustainability, opting for low-E glass supports environmentally friendly building practices.
Applications of Low-E Glass
Low-E glass is versatile and can be employed in various settings. It is commonly used in residential windows, where homeowners seek to increase energy efficiency and comfort. In commercial buildings, low-E glass is often employed in curtain walls and storefronts, contributing to attractive, energy-efficient facades.
In addition, low-E glass is widely used in skylights and sunrooms, where maximizing natural light while minimizing unwanted heat gain is essential. The automotive industry has also begun integrating low-E glass in vehicles, providing better climate control and enhancing passenger comfort.
Conclusion
In summary, low-E glass materials represent a significant advancement in building technology, providing numerous benefits that contribute to energy efficiency, occupant comfort, and sustainability. With diverse applications ranging from residential to commercial use, low-E glass is a valuable component for modern buildings seeking to reduce their environmental footprint while maintaining aesthetic appeal. As society continues to move towards greener solutions, low-E glass will undoubtedly play a crucial role in shaping energy-efficient architecture of the future.