

Understanding Dead Flat Float Glass Properties and Applications
Dead flat float glass, a type of glass renowned for its clarity and smoothness, plays a crucial role in various architectural and industrial applications. Unlike regular glass, dead flat float glass is designed to achieve an exceptional level of flatness. This attribute is critical in applications where visual clarity and aesthetic appeal are paramount. This article explores the properties, manufacturing process, and applications of dead flat float glass.
What is Dead Flat Float Glass?
Dead flat float glass is produced through the float glass process, where molten glass is poured onto a molten tin bath. This method results in a glass sheet with uniform thickness and a perfectly smooth surface. The term dead flat refers to the glass's ability to remain perfectly even across its surface without any distortions or waves. This flatness is measured in microns, and the glass typically maintains a deviation of less than 1 micron over its entire surface area.
One of the key characteristics of dead flat float glass is its optical clarity. The manufacturing process eliminates impurities and inclusions, resulting in a glass that provides clear visibility and minimal light distortion. This quality makes it an ideal choice for uses where transparency is essential, such as in retail displays, office partitions, and high-end architectural designs.
Manufacturing Process
The manufacturing of dead flat float glass involves several steps. First, raw materials such as silica sand, soda ash, and limestone are melted in a furnace at high temperatures. The molten glass is then carefully poured onto a moving surface of molten tin. Because glass is less dense than tin, it floats on the surface, forming a sheet that is perfectly level. The sheet is slowly cooled in a controlled environment to prevent stress fractures and ensure robustness.
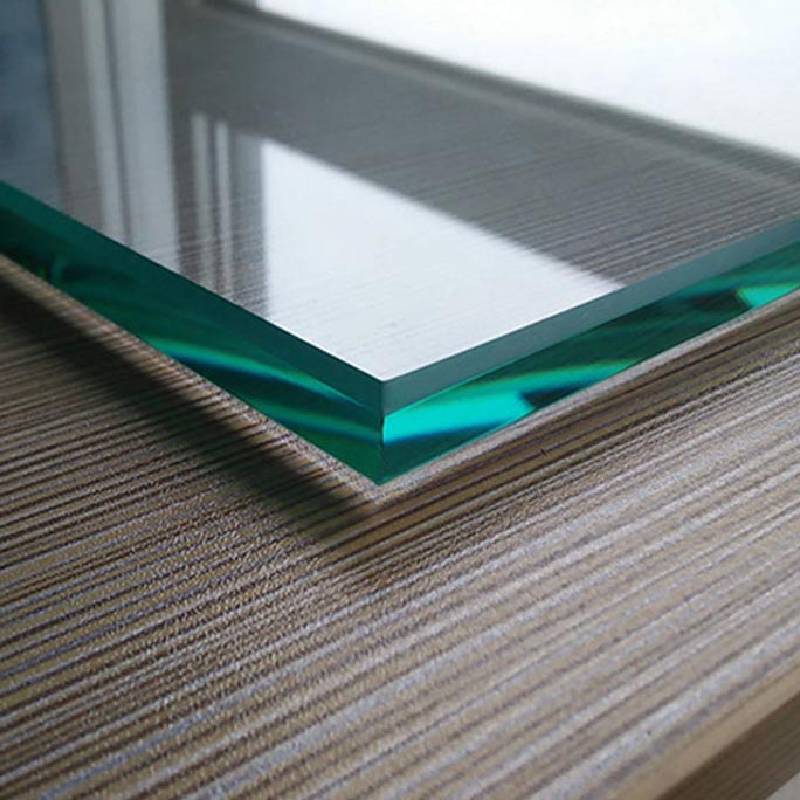
Once cooled, the glass is cut into specified sizes and can undergo further treatments, such as polishing or coating, to enhance its durability and performance. Additional processes, such as laminating or tempering, can also be applied depending on the end-use requirements.
Applications of Dead Flat Float Glass
Dead flat float glass has a wide range of applications across various industries. In the construction sector, it is used in large windows, facades, and glass walls, where aesthetic appeal and energy efficiency are crucial. Its optical clarity makes it ideal for use in museums and galleries, where preserving the integrity of artwork and artifacts is essential.
In the automotive industry, dead flat float glass is utilized in windshields and side windows, providing safety and visibility. In electronics, it serves as substrates for screens and displays, ensuring a high-quality visual experience.
Moreover, the furniture industry leverages dead flat float glass in tabletops and shelving units, combining function with modern design aesthetics.
Conclusion
Dead flat float glass is more than just a material; it represents the intersection of functionality, aesthetics, and innovative manufacturing processes. Its exceptional flatness and clarity open up a world of possibilities across various fields, making it a preferred choice for architects, designers, and manufacturers alike. As technology advances and new applications are discovered, the significance of dead flat float glass in modern society will undoubtedly continue to grow.