

The Evolution and Impact of Float Flat Glass in Modern Architecture
In the realm of modern architecture, the emergence of float flat glass has revolutionized the way structures are designed and constructed. This innovative material, known for its clarity, uniformity, and versatility, has become a staple in both residential and commercial buildings. Its production process, aesthetic qualities, and functional benefits have made float flat glass integral to contemporary design.
Float glass, created through the process of floating molten glass on molten tin, exhibits a smooth, flat surface that is free from distortions. This method, developed in the 1950s by Sir Alastair Pilkington, set a new standard in glass manufacturing. The result is a product that not only possesses exceptional optical clarity but is also available in large sheets, allowing architects to create expansive windows and glass facades that were previously unattainable. The uniform thickness and strength of float glass have paved the way for innovative design possibilities, enabling architects to experiment with light, transparency, and space in unprecedented ways.
The aesthetic qualities of float flat glass are profound. Buildings like the Louvre Pyramid in Paris and the Apple Park in Cupertino, California, demonstrate how glass can create a seamless connection between the interior and exterior, blurring the lines between structure and nature. The reflective surface of float glass can enhance the visual impact of buildings, allowing them to shimmer and change with the shifting light throughout the day. This natural interplay of light and shadow not only adds to the beauty of a building but also impacts the overall mood and atmosphere of the space within.
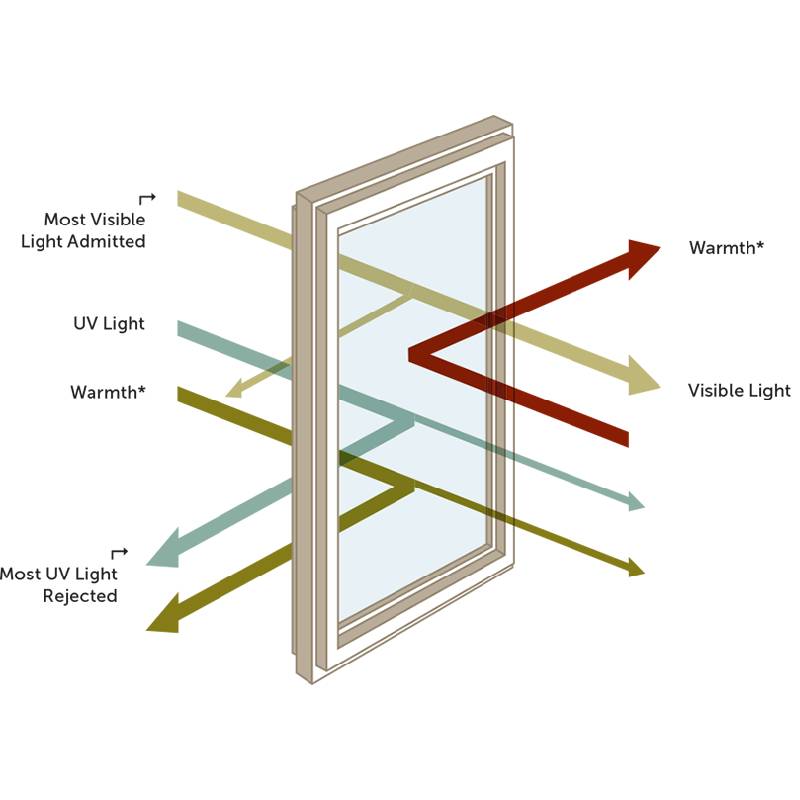
Functional benefits of float flat glass are equally significant
. One of the primary advantages of this material is its ability to enhance energy efficiency. With advancements in glass technology, including the development of low-emissivity (low-e) coatings, float glass can effectively reflect heat while allowing natural light to penetrate. This results in reduced energy consumption for heating and cooling, making buildings more sustainable and environmentally friendly. Furthermore, float glass is highly durable and resistant to weathering, which contributes to the longevity and maintenance of structures.Safety features of float flat glass have also evolved. Today, buildings often incorporate tempered or laminated glass, which provides increased strength and resistance to breakage. In the event of an accident, these types of glass shatter into small, blunt pieces rather than sharp shards, reducing the risk of injury. This commitment to safety ensures that float flat glass can be used in a variety of applications, from storefronts to high-rise buildings.
Additionally, float glass is an inherently abundant material, and advancements in recycling processes have made it an even more sustainable choice. The glass industry has made significant strides in reducing waste through recycling programs, further enhancing the environmental benefits of using float flat glass in construction.
In conclusion, float flat glass has significantly impacted modern architecture, providing architects with the tools necessary to create stunning and functional spaces. Its production method ensures a high-quality product that meets the aesthetic and practical demands of contemporary design. As technology continues to evolve, the applications and advantages of float flat glass are likely to expand, further reshaping the landscapes of our cities and revolutionizing architectural practices. By embracing this innovative material, designers not only enhance the beauty of our built environment but also contribute to a more sustainable future.