

Understanding Low-E Glass Costs Benefits and Considerations
Low emissivity (Low-E) glass has gained immense popularity in the construction and renovation of residential and commercial buildings. This specialized glass is designed to minimize the amount of infrared and ultraviolet light that passes through it without compromising visible light. In simpler terms, it reflects heat back into a room during winter and keeps it out during summer, making it a highly energy-efficient option. However, with increasing adoption comes a keen interest in understanding the costs associated with Low-E glass, which can influence the decision-making process for builders and homeowners alike.
What is Low-E Glass?
Low-E glass is treated with a microscopically thin coating that reflects heat. This technology can significantly improve a building’s energy efficiency, reducing the need for heating and cooling and, consequently, lowering utility bills. There are two main types of Low-E coatings hard-coat and soft-coat. Hard-coat Low-E glass is typically more durable and suitable for warmer climates, while soft-coat Low-E glass performs better in colder climates due to its higher insulating properties.
Cost Factors
When considering Low-E glass, several factors will determine the overall cost
1. Type of Low-E Glass Hard-coat glass tends to be less expensive than soft-coat glass. However, the choice between the two will largely depend on climate and the specific energy efficiency requirements of the building.
2. Window Size and Design The dimensions and architectural style of the windows will also impact costs. Larger and uniquely shaped windows require more material and labor, increasing the overall price.
3. Additional Features Some manufacturers offer Low-E glass with enhanced features, such as triple glazing or gas fills for improved insulation. While these features can drive up costs, they can lead to higher energy savings over time.
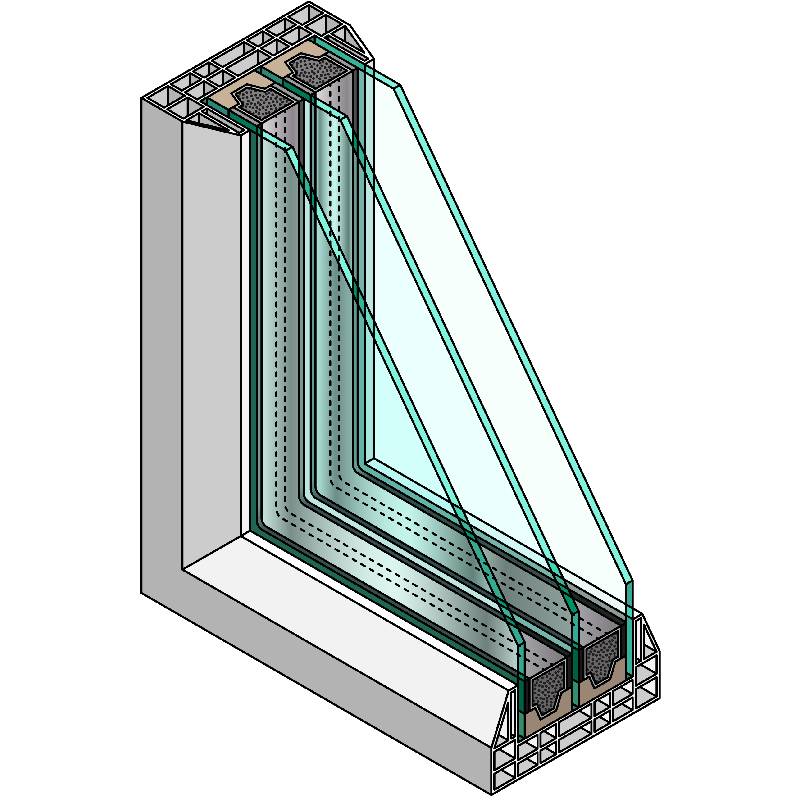
4. Installation Costs Professional installation is crucial to ensure that Low-E glass performs as intended. This can add to the total cost, especially if the installation involves structural modifications.
5. Bulk Purchasing For larger construction projects, purchasing Low-E glass in bulk can result in significant discounts, lowering the per-unit cost.
Cost Benefits
Despite the initial investment, Low-E glass can lead to long-term savings. Homes and buildings equipped with Low-E glass typically experience reduced heating and cooling costs. In a more energy-efficient environment, homeowners may also benefit from tax credits and rebates offered for energy-saving home improvements, further offsetting the installation costs.
Additionally, Low-E glass can enhance indoor comfort by reducing temperature fluctuations and minimizing glare. The improved thermal performance can result in a more stable indoor climate, which is especially valuable in extreme weather conditions.
Conclusion
While the cost of Low-E glass can be higher than conventional glass options, the long-term benefits often justify the investment. By reducing energy consumption and enhancing comfort, Low-E glass is not only a smart choice for environmentally conscious builders and homeowners but also an economically sound decision over time.
When evaluating the costs associated with Low-E glass, it is essential to consider both immediate expenses and future savings. Consulting with a knowledgeable contractor or window specialist can provide insights tailored to specific project needs, making it easier to weigh the benefits against the costs. As energy efficiency becomes increasingly important in building design, Low-E glass stands out as a valuable component that can enhance property value while contributing to a sustainable future.