Float glass, an essential building material, boasts a precise manufacturing process that has transformed modern construction and design. Its intrinsic properties make it indispensable for various applications, from windows to sophisticated architectural projects.

At its core, float glass is named after the “floating” technique employed during its production. In the late 1950s, Sir Alastair Pilkington from the UK revolutionized the traditional glass-making method, introducing the floating process. This innovative approach involves pouring molten glass onto a bed of molten tin within a controlled atmosphere. As the glass spreads over the tin, it forms a uniform thickness, resulting in perfectly flat glass with parallel surfaces, free from distortions. This uniformity is crucial, as it allows for unparalleled clarity and performance in its applications.
The versatility of float glass arises from its mechanical and visual properties. Architects and engineers favor this type of glass due to its smooth surface and flawless finish. The transparency of float glass ensures maximum light penetration, making it a preferred choice in designs requiring abundant natural light. This characteristic not only enhances aesthetic appeal but also contributes to energy efficiency by reducing the need for artificial lighting.
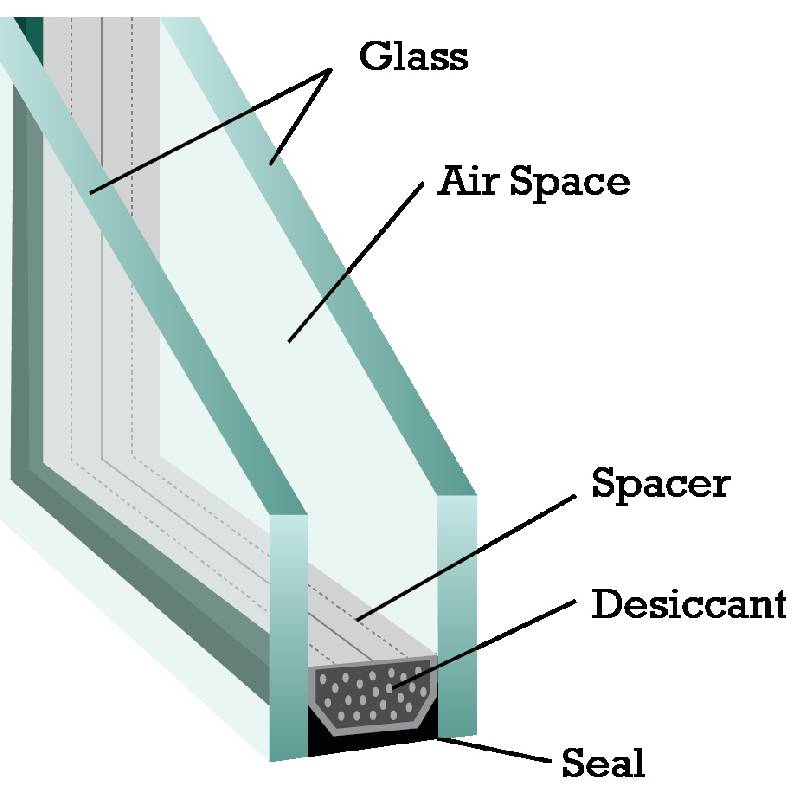
Moreover, float glass serves as the foundation for various advanced glass products. Through additional processing, it can be transformed into laminated, toughened, or insulated glass, each with its specific advantages. Laminated glass, for example, enhances safety by preventing shattering upon impact, whereas toughened glass offers increased strength and thermal resistance. Insulated glass units (IGUs) are fabricated by combining multiple panes of float glass, significantly improving thermal insulation and soundproofing capabilities.
Environmental considerations have also propelled technological advancements in float glass production. Modern facilities integrate sustainable practices, such as using recycled glass, known as cullet, which reduces energy consumption and raw material use. These efforts underscore the industry’s commitment to reducing its ecological footprint while maintaining product quality.
what is float glass
In terms of expertise, the float glass sector continuously pushes the boundaries of innovation. Researchers are exploring coatings that enhance the glass's properties, such as low-emissivity coatings that improve thermal performance by reflecting infrared heat. This not only contributes to energy-saving efforts but also offers consumers better control over interior climates, leading to increased comfort and reduced energy costs.
Authoritativeness in the field of float glass manufacturing is exemplified by adhering to strict quality standards. International organizations and regulatory bodies, such as the ISO, set these benchmarks to ensure consistency, durability, and safety of glass products globally. Manufacturers who align with these standards demonstrate their commitment to quality and consumer trust.
Gaining insight from real-world applications further bolsters the case for float glass as an unmatched material in construction and design. Iconic structures worldwide, from skyscrapers to high-end residential complexes, showcase float glass's applications, underscoring its role in modern architecture. Designers appreciate float glass for its ability to blend seamlessly with other materials, providing endless possibilities in aesthetic expression.
In essence, float glass embodies a blend of historical innovation, ongoing advancements, and practical applications. Its role in efficient energy use and sustainable practices highlights the importance of continued research and development. As the demand for quality, sustainable construction materials rises, float glass remains pivotal, driven by its unmatched clarity, adaptability, and potential for further innovation.



